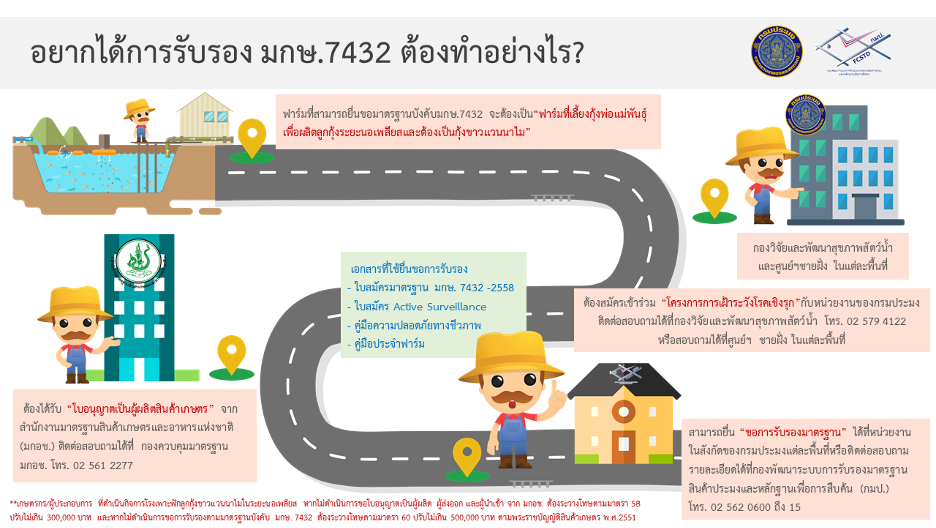
Introduction
The Thai Agricultural Standard (TAS 7432-2015), Good Aquaculture Practices for Hatchery of Disease-Free Pacific White Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei), has been established to provide guidance for disease-free shrimp hatchery operations, including water management, feed quality, hygienic practices, and disease prevention measures within farms, in order to produce high-quality and safe shrimp for both domestic and international markets. Since the culture of Pacific white shrimp in Thailand has encountered serious disease problems, particularly Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease (AHPND) in Pacific white shrimp juveniles, which has caused severe losses to shrimp farmers, it is therefore necessary to control the hatchery production of Pacific white shrimp to prevent disease transmission from broodstock to nauplii and to control the spread of diseases within hatcheries.


Objective
In order for Pacific white shrimp hatcheries to operate in compliance with the standard, covering from broodstock receiving, nauplius production, up to the movement of shrimp postlarvae out of the hatchery.
Scope
- This agricultural standard covers hatcheries producing Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) at the nauplius stage.
- มาตรฐานสินค้าเกษตรนี้ กำหนดเกณฑ์การปฏิบัติที่ดีสำหรับการเพาะลูกกุ้งขาวแวนนาไมในระยะนอเพลียส ตั้งแต่การรับพ่อแม่พันธุ์กุ้งขาวแวนนาไมไปจนถึงก่อนการเคลื่อนย้ายลูกกุ้งขาวแวนนาไมระยะนอเพลียส ออกจากบ่อฟักหรือภาชนะอื่นที่ใช้ในการฟัก เพื่อให้ได้ลูกกุ้งขาวแวนนาไมระยะนอเพลียสปลอดจากโรค

Key points of Good Aquaculture Practices for Hatchery of Disease-Free Pacific White Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei)
Summary of the Thai Agricultural Standard (TAS 7432-2015): Good Aquaculture Practices for Hatchery of Disease-Free Pacific White Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei)
7 requirements as stipulated under the mandatory standard
1. Production principles
- Availability of a biosecurity manual
- Participation in the disease surveillance program
- Free from “designated diseases under the standard” for at least 6 consecutive months
- White spot disease (WSD)
- Yellow head disease (YHD)
- Taura Syndrome (TS)
- Infectious hypodermal and haematopoietic necrosis virus disease (IHHNV)
- Infectious myonecrosis (IMN)
- Early mortality syndrome (EMS)
2. Personnel
- Farmers have knowledge and be trained and/or have experience.
- Control measures for personnel and visitors to prevent the introduction and spread of pathogens shall be in place.


3. Selection of disease-free Pacific white shrimp broodstock
- Broodstock shall be free from the designated diseases under the standard.
- An effective quarantine system for broodstock shall be in place.
4. General management
- An operating manual for the hatchery shall be available.
- Broodstock housing and quarantine areas shall be operated in closed facilities.
- Tools and equipment for each zone shall be separated and properly disinfected according to technical methods.
- Water used in the hatchery shall be of suitable quality and disinfected in accordance with technical methods.
- Vehicles shall be disinfected at the farm entry and exit.
- Pests shall be controlled and prevented from entering the hatchery production areas.
- No pet shall be allowed in the production areas of the hatchery.
- Rubbish and waste shall be collected and discarded hygienically.
- Waste from toilets shall be discarded hygienically to prevent contamination.
5. Feed management for Pacific white shrimp broodstock
- Registered formulated feed in accordance with the Animal Feed Quality Control Act B.E. 2525 (1982) shall be used. On-farm and/or natural feed may be used provided that it is hygienically prepared and accompanied by an inspection report confirming it is free from designated diseases.
- Feed shall be stored in an appropriate place to prevent contamination and maintain its quality.
6. Pacific white shrimp health management
- Measures shall be in place to prevent and control the spread of shrimp diseases.
- Inspection report of shrimp random sampling shall indicate freedom from the designated diseases.
- In case shrimp mortality caused by disease outbreak is found, disease transmission shall be controlled and the competent authority shall be immediately informed.
7. Records
- Records of the production process shall be kept for at least three years.
Examples include rearing records, feed records, water quality records, etc.

Enforcement
This standard shall be enforced as a mandatory standard for Pacific white shrimp hatcheries nationwide. Failure to comply with this standard may result in suspension of operations and be subject to a fine.
Good Aquaculture Practice requirements for hatchery of disease-free Pacific white shrimp (TAS 7432-2015)
- This agricultural standard covers hatcheries producing Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) at the nauplius stage.
- This agricultural standard establishes requirements on good aquaculture practices for the production of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) at the nauplius stage, covering from broodstock receiving up until before the movement of nauplii from the hatching pond or other hatching containers, in order to obtain nauplii free from the designated diseases.